
Acute Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation Lowers IL-2R Signaling and the Proliferative Potential of Regulatory T Cells | ImmunoHorizons
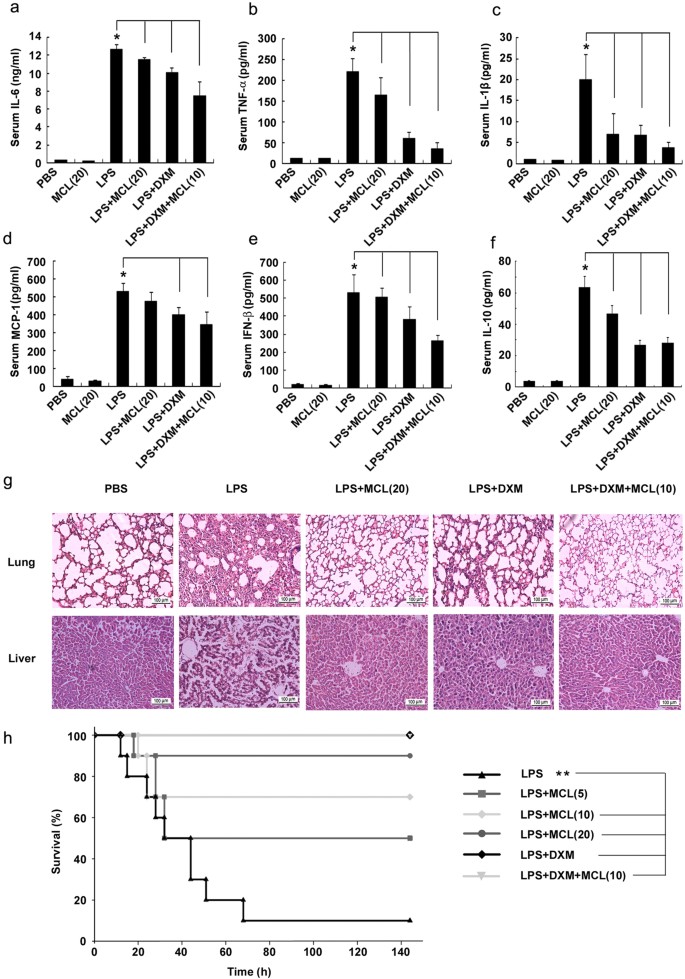
Micheliolide inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response and protects mice from LPS challenge | Scientific Reports
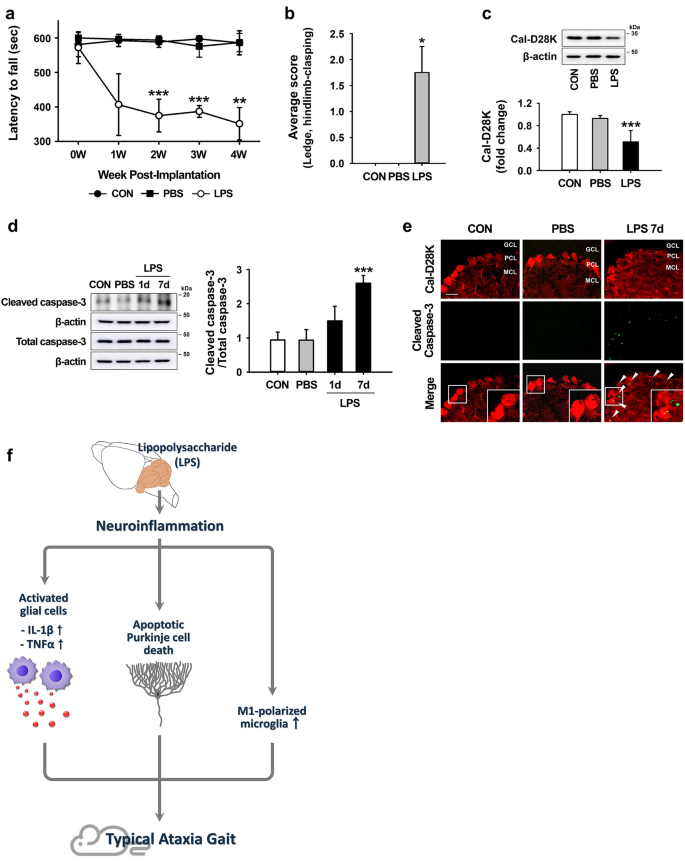
Lipopolysaccharide administration for a mouse model of cerebellar ataxia with neuroinflammation | Scientific Reports
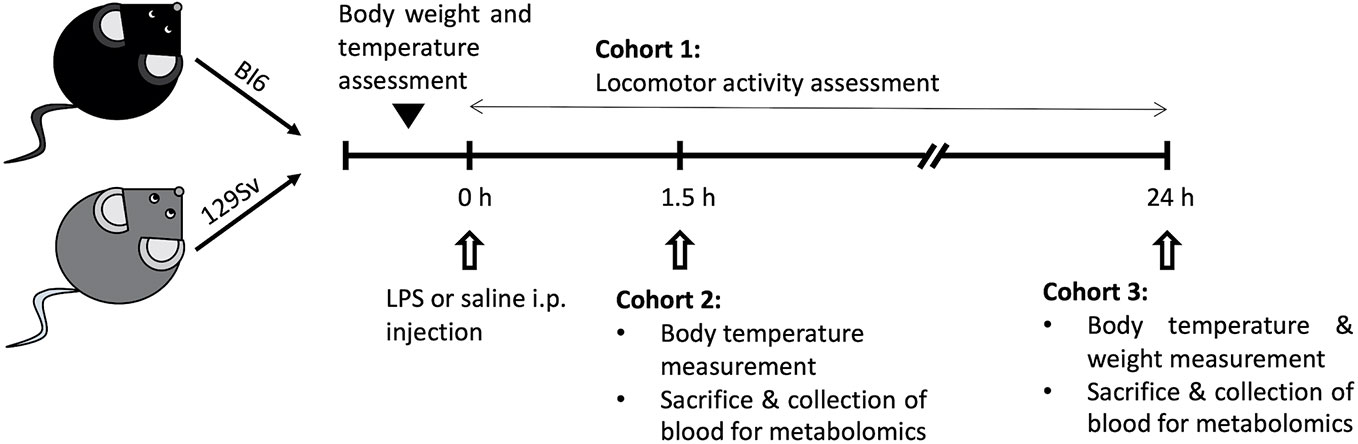
Frontiers | Treatment With Lipopolysaccharide Induces Distinct Changes in Metabolite Profile and Body Weight in 129Sv and Bl6 Mouse Strains | Pharmacology

Rolipram Protects Mice from Gram-negative Bacterium Escherichia coli-induced Inflammation and Septic Shock | Scientific Reports
Expression of proinflammatory cytokines in the LPS-induced mouse model... | Download Scientific Diagram

Glucosamine improves survival in a mouse model of sepsis and attenuates sepsis-induced lung injury and inflammation - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Septic Shock Is Associated with Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products Ligation of LPS | The Journal of Immunology
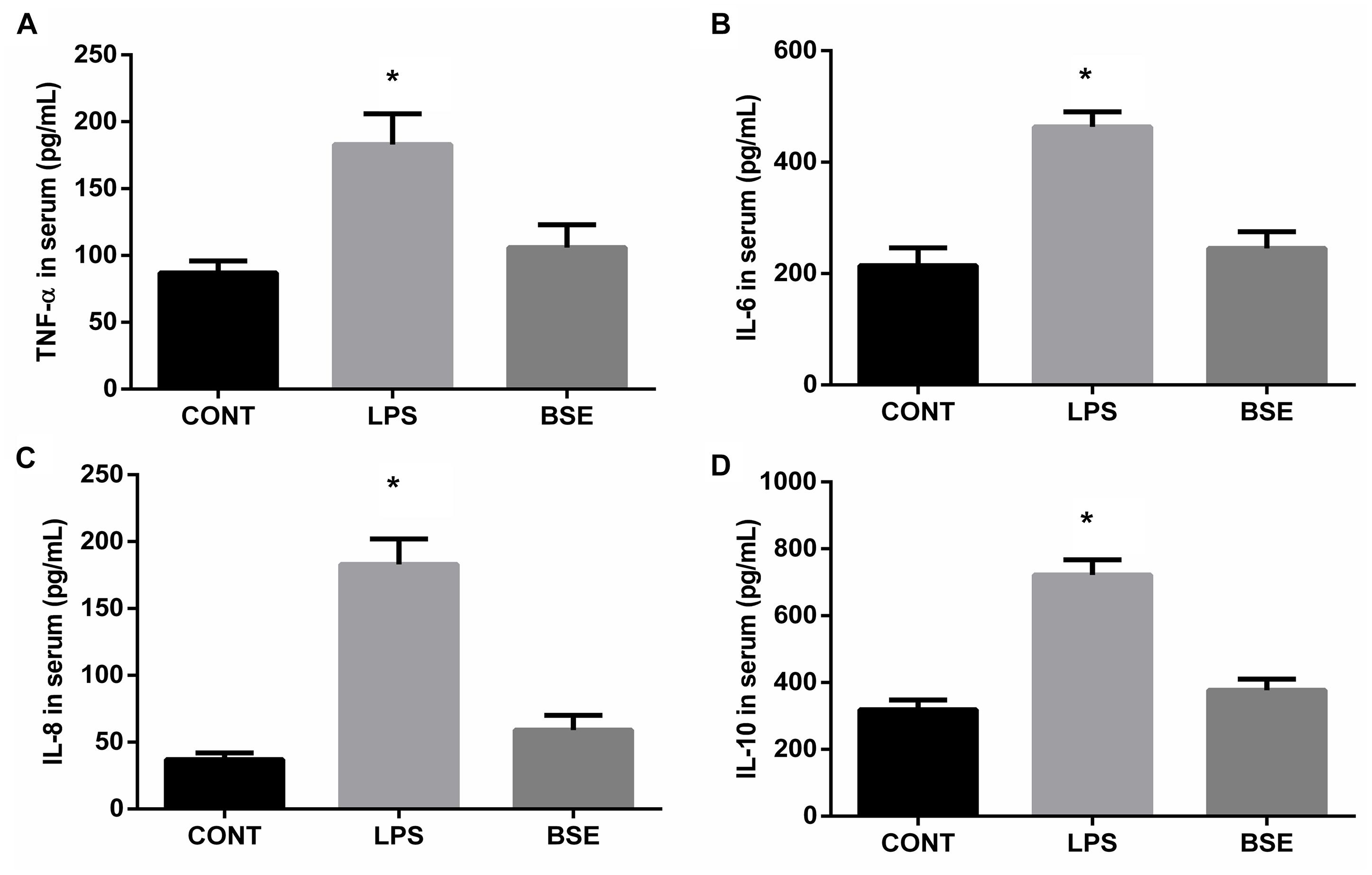
Frontiers | Effects of Blidingia sp. Extract on Intestinal Inflammation and Microbiota Composition in LPS-Challenged Mice | Physiology
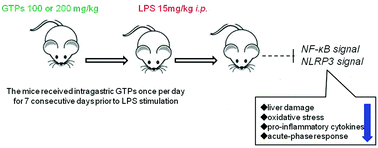
Green tea polyphenols prevent lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory liver injury in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation - Food & Function (RSC Publishing)

Anti-inflammatory Effects of Exosomes in a Mouse Model of LPS-Induced... | Download Scientific Diagram

A) Schematic illustration of the acute LPS-induced inflammation mouse... | Download Scientific Diagram
Lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia in corn oil-preloaded mice causes an extended course of lung injury and repair and pulmonary fibrosis: A translational mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome | PLOS ONE

Injections of Lipopolysaccharide into Mice to Mimic Entrance of Microbial-derived Products After Intestinal Barrier Breach | Protocol

Intraductal Injection of LPS as a Mouse Model of Mastitis: Signaling Visualized via an NF-κB Reporter Transgenic | Protocol

Effects of tamarixetin on an LPS-induced endotoxemia mouse model. (A)... | Download Scientific Diagram

Exosomal delivery of NF-κB inhibitor delays LPS-induced preterm birth and modulates fetal immune cell profile in mouse models

Frontiers | Microglial Ultrastructure in the Hippocampus of a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sickness Mouse Model | Neuroscience

Lactobacillus pentosus S-PT84 prevents LPS-induced low-grade chronic inflammation in a C57BL/6J mouse model - ScienceDirect

Lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis induces long-lasting affective changes in the mouse - ScienceDirect

.jpg)



